Abstract
Introduction. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is becoming the standard of care for patients with aggressive B cell lymphoma (ABCL), including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and high-grade B cell lymphoma (H-GBCL) pre-treated with 2 lines. We have recently reported real-world data in Spain, with efficacy results similar to those reported in the pivotal studies and other real-world experiences. It is known that patients with SCHOLAR-1 refractoriness criteria have a particularly poor prognosis with any treatment, so, the objective of this analysis is to evaluate the impact of SCHOLAR-1 refractoriness criteria on efficacy compared to non-refractory population.
Methods This is a multicenter, retrospective, observational study that included all patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) ABCL treated with CAR-T therapy in Spain and registered in the GELTAMO/GETH database (n=404). The main objective was to analyze efficacy in terms of response rates and survival for ABCL patients with or without SCHOLAR-1 criteria (primary refractoriness, refractoriness to last treatment, or early relapse after autologous stem-cell transplant [SCT]), comparing both commercial products axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) and tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel).
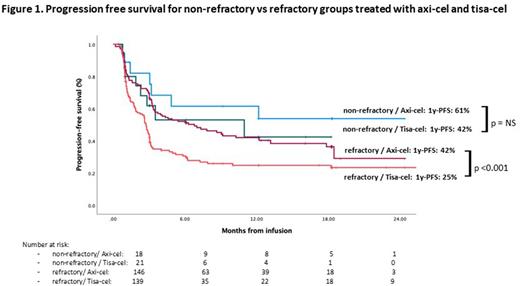
Results From the 404 patients with ABCL registered, 20 were excluded due to absence of follow-up data and 31 for primary mediastinal lymphoma histology; finally, 353 patients were included for the primary analysis; 324 (91%) received the CAR-T cell infusion (164 axi-cel and 160 tisa-cel). Patient characteristics at infusion were balanced for both CAR-T products except for younger age (57 [23-79] vs 63 [23-79], p=0.02) and more patients with bulky disease (73 [46%] vs 43 [28%], p= 0.001) in the axi-cel group. With a median follow-up from infusion of 12.2 months (95%CI:11.3-13), median progression-free survival (PFS) was 3.3 months (95%CI: 2.4-4.2), and median overall survival (OS) was 15.2 months (95%CI: 10.7-19.7) for the whole infused cohort. For the infused patients 285 (88%) met at least one SCHOLAR-1 criteria (146 [52%] axi-cel y 139 [48%] tisa-cel) and 39 (11%) were non-refractory (18 [46%] axi-cel y 21 [54%] tisa-cel). There were no significant differences in patient characteristics between SCHOLAR-1 and non-refractory groups, except for a higher rate of bulky disease in the SCHOLAR-1 patients (39% vs 9%, p=0.001). Median OS was 12.3 months (95%CI: 9-15.6) and median PFS was 3.2 months (95%CI: 2.7-3.8) in the refractory group, whereas median OS and PFS were not reached (1 year-OS: 81%; 1 year-PFS: 54%) in the non-refractory group. In the SCHOLAR-1 group, comparing axi-cel and tisa-cel, 1 year-PFS was 42% and 25% (p=0.005) (Figure 1), and 1 year-OS was 60% and 39% (p=0.001), respectively. For non-refractory patients, 1 year-PFS was 87% and 77% (p=0.37) (Figure 1) and 1 year OS was 64% and 42% (p=0.35) for axi-cel and tisa-cel, respectively. In the multivariate analysis for the Sholar-1 cohort, factors independently influencing PFS were: CAR-T tisa-cel (HR 1.7 [CI:1.23-2.34, p=02001]), having received bridging therapy (HR 1.72 [CI: 1.08-1.27, p= 0.22], refractoriness to last treatment (HR 2.04 [CI: 1-17-3.55]), HCTCI ≥2 pre-infusion (HR 1.6 [CI: 1.19-2.29]), and for OS: CAR-T tisa-cel ( HR 1.74 [CI: 1.12-2.7, p= 0.012]), ECOG ≥2 pre-apheresis ( HR 2.4 [CI:1.11-5-47, p= 0.02]), previous auto-SCT ( HR 2.22 [CI:1.4-3.52, p= 0.001]). In terms of toxicity, 82% of patients had cytokine release syndrome (CRS) (6% ≥ grade 3), and 33% of patients had Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) (11% ≥ grade 3). Rates of CRS and ICANS were no different between refractory and non-refractory patients. CRS rate was 71% and 93% and CRS ≥ grade 3 rate was 4% and 8% (p=0.001) for tisa-cel and axi-cel respectively. ICANS rate was 16% and 50%, and ICANS ≥ grade 3 rate was 4% and 18% (p=0.001), respectively. Non-relapse mortality was 5% and 7% for tisa-cel and axi-cel respectively (p= 0.64).
Conclusions: We conclude that SCHOLAR-1 refractoriness criteria influence notably the CAR-T cell therapy efficacy. In our experience, axi-cel showed better results in terms of efficacy than tisa-cel for this population, but also significantly more toxicity. Results for non-refractory patients are significantly better with both products, but the small sample size prevents reaching solid conclusions in this population.
Disclosures
Bastos-Oreiro:INCYTE: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; KITE/GILEAD: Consultancy, Honoraria; NOVARTIS: Speakers Bureau; JANSSEN: Speakers Bureau. Iacoboni:NOVARTIS, KITE/GILEAD, BMS/CELGENE: Consultancy; NOVARTIS, KITE/GILEAD, BMS/CELGENE, ASTRAZENECA, ROCHE, ABBVIE, JANSSEN, MILTENYI: Honoraria. Terol:Janssen, Abbvie, Roche, Takeda, Astra-Zeneca: Consultancy. Abrisqueta:Incyte: Consultancy; Sandoz: Honoraria; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Mussetti:GILEAD: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy; JAZZ PHARMACEUTICALS: Consultancy; TAKEDA: Honoraria. Jimenez-Ubieto:Novartis: Consultancy. Sancho:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria; BeiGene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celltrion: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Eli Lilly & Company: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Miltenyi Biomedicine: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sandoz: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kern Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria. Sureda:TAKEDA: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; JANSSEN: Consultancy, Honoraria; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; MSD: Honoraria; ROCHE: Consultancy, Honoraria; SANOFI: Consultancy, Honoraria; NOVARTIS: Consultancy, Honoraria; GILEAD: Consultancy. Barba:Allogene, Amgen, BMS, Gilead, Incyte, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Miltenyi Biomedicine, Nektar and Novartis: Consultancy. Martín García-Sancho:Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Gilead/Kite: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Eusa Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Clinigen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Kyowa Kirin: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Incyte: Consultancy, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Lilly: Consultancy, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Miltenyi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; ADC Therapeutics America: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Kern: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.